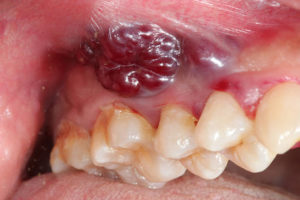
Tooth decay and gum disease aren’t the only threats to your smile. 54,500 Americans are diagnosed with oral cancer each year, which is responsible for over 11,500 deaths annually. The 5-year survival rate is only 67%, which is attributed to late detection. Contrary to what you might have heard, you don’t have to be a smoker to be at risk. Oral cancer can affect anyone. Here’s what you need to know to safeguard your smile.
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is classified as those affecting the mouth, throat, and neck. Although it’s easy to detect during the earliest stages, it often isn’t found until it has metastasized. There are 5 stages of mouth cancer, which include:
Stage 0
The very beginning stage of oral cancer is called carcinoma in situ, which means there are abnormal cells in the lining of the oral cavity or lips that have the potential to become cancer.
Stage I
A tumor that is no more than 2 centimeters in size and hasn’t spread to the lymph nodes is classified as stage I mouth cancer.
Stage II
Stage II mouth cancer is described as a tumor between 2-4 centimeters and hasn’t reached the lymph nodes.
Stage III
A tumor that’s larger than 4 centimeters or has spread to the lymph nodes is categorized as stage III.
Stage IV
The more advanced stage of mouth cancer can affect nearby tissue, one or more lymph nodes, or other areas of the body, like the lungs. Stage IV mouth cancer can come back after treatment in other parts of the body.
Regular oral cancer screenings are the best way to detect precancerous and cancerous cells early. It’s estimated that 80% of new oral cancer cases can be diagnosed early through routine screenings performed by a dentist at semi-annual cleanings and checkups.
Treating Oral Cancer
There are many ways to treat oral cancer, depending on the stage and location. Common treatments can include:
- Surgery to remove the affected tissue.
- Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy with drugs to kill cancerous cells.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
No one is immune to oral cancer, but there are known factors that can increase your risk, like:
- Human papillomavirus infection.
- Chronic facial sun exposure.
- Previous oral cancer diagnosis.
- Family history of oral and other types of cancer.
- A weakened immune system.
- Poor nutrition.
- Certain genetic syndromes.
- Being male.
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Symptoms of oral cancer can be diverse and appear in many ways, like:
- Oral sores that won’t heal.
- Growths or masses.
- Oral bleeding.
- Loose teeth.
- Difficult swallowing.
- Persistent earache.
- Facial numbness.
- White, red, white, or rough patches of tissue.
Besides monitoring for symptoms at home, visit your dentist regularly for an oral cancer screening to benefit from the power of early detection.
About Dr. Alex Naini
Dr. Naini earned her dental degree from the University of Maryland Dental School in Baltimore and has regularly continued her education in many advanced services. She focuses on prevention to help each patient achieve optimal oral health. If you need an oral cancer screening, request an appointment through our website or call (703) 827-8282.
